
The Essence of Private Debt:A Comprehensive Overview
In the complex world of finance, various investment options cater to different risk appetites and return expectations. One avenue gaining traction in recent years is private debt. While it may sound obscure, understanding its role can shed light on a crucial part of the financial landscape. In this blog, Rodller will delve into the intricacies of private debt, exploring its definition, functionalities, benefits, drawbacks, and comparisons to other investment approaches.
Defining Private Debt
At its core, private debt refers to debt financing extended to companies through private channels, bypassing traditional avenues like banks or public markets. These loans are typically provided by specialized investment funds or institutions managing capital from various investors. Unlike publicly traded securities, private debt instruments are not readily available for buying and selling on stock exchanges.
Key characteristics of private debt:
- Non-bank lending: Bypasses traditional bank loans.
- Illiquid: Investments are not easily bought and sold.
- Structured loans: Tailored terms based on borrower and lender needs.
- Direct lending: Investment funds directly manage loan agreements.
Who Operates in the Private Debt Market?
The private debt ecosystem involves several key players:
- Borrowers: Companies seeking financing for various purposes like growth, acquisitions, or restructuring.
- Lenders: Investment funds, insurance companies, and asset managers specializing in private debt.
- Fund managers: Experts responsible for sourcing, structuring, and managing private debt investments.
- Intermediaries: Legal and financial advisors facilitating negotiations and transactions.
Why Choose Private Debt?
Several advantages attract investors to private debt, including:
- Potentially higher yields: Compared to traditional bonds, private debt can offer attractive interest rates.
- Diversification: Provides an alternative asset class to diversify portfolios and mitigate overall risk.
- Lower volatility: Private debt often exhibits lower volatility than publicly traded equities, offering relative stability.
- Structured covenants: Loan agreements often include covenants protecting lenders in case of borrower performance issues.
- Direct influence: Fund managers can influence borrower behaviour through negotiation and ongoing monitoring.
Potential Challenges in Private Debt
While offering promising benefits, private debt also comes with limitations:
- Illiquidity: Difficulty in selling investments before maturity can impact immediate cash needs.
- Higher minimum investment: Entry often requires a significant initial investment, making it less accessible to smaller investors.
- Complex due diligence: Thorough research and analysis are crucial due to the non-public nature of the investments.
- Dependence on fund managers: Investor returns rely heavily on the expertise and skill of the chosen fund manager.

Private Debt vs. Private Equity
Though both involve private capital, private debt and private equity represent distinct financial instruments:
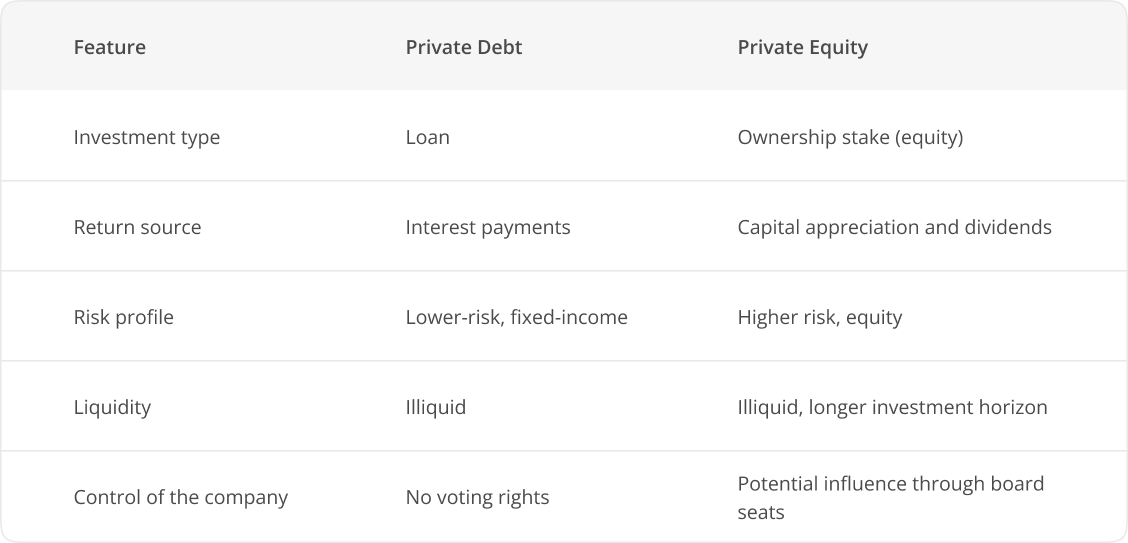
Is Private Debt Right for You?
Before venturing into private debt, investors should carefully consider several factors:
- Investment goals: Aligning with one’s risk tolerance and return expectations.
- Investment horizon: Accepting the illiquidity nature of private debt investments.
- Understanding the market: Gaining knowledge of the complexities and risks involved.
- Seeking professional guidance: Consulting qualified financial advisors for personalized recommendations.
By understanding the fundamentals, benefits, and limitations of private debt, individuals can make informed investment decisions. In the evolving financial landscape, private debt presents a unique opportunity for achieving diversification and potentially higher returns while recognizing the associated risks and complexities.
Having grasped the core principles of private debt, let’s delve deeper into its diverse forms and applications:
Types of Private Debt:
- Senior Debt: This is the least risky type, offering the highest priority in repayment in case of default. It carries a lower interest rate compared to other types.
- Mezzanine Debt: Sitting between senior and junior debt in the capital structure, mezzanine debt offers higher risk and returns than senior debt.
- Junior Debt: The riskiest type of private debt, with the highest potential return but also the highest risk of default. Often referred to as “high-yield” or “junk bonds.”
- Unitranche Loans: Combining features of senior and mezzanine debt, these loans offer a single stream of principal and interest payments.
- Direct Lending: Investment funds directly originate and manage loans, providing greater control over the investment.
Applications of Private Debt:
- Financing Corporate Growth: Companies seeking to expand operations, invest in new technologies, or make acquisitions can utilize private debt.
- Leveraged Buyouts (LBOs): Private debt plays a crucial role in financing LBOs, where investors acquire a company using a significant amount of borrowed capital.
- Restructuring Debt: Companies facing financial difficulties can utilize private debt to restructure existing debt and improve their financial health.
- Infrastructure Projects: Private debt can help finance the development and construction of essential infrastructure projects.
Evolution of the Market:
- Growth: The private debt market has witnessed significant growth in recent years, driven by factors like low interest rates and increased demand for alternative investment options.
- Technology and Innovation: Technological advancements are streamlining and democratizing access to private debt, potentially making it more accessible to a wider range of investors.
- Regulation: Regulatory changes can impact the structure and risk profile of private debt investments. It is very important to stay updated on the latest regulatory developments.

Conclusion:
Let Rodller sum up: Private debt offers a unique and potentially lucrative avenue for investors seeking diversification and attractive returns. However, its complexities and inherent risks necessitate thorough research, professional guidance, and a well-defined investment strategy. By understanding the various types, applications, and evolving landscape of private debt, individuals can make informed decisions and position themselves to navigate this dynamic and increasingly important financial sector.
About Rodller
Rodller (www.rodller.com) provides Digital Marketing, Fundraising and Application Development Services. With offices in Singapore and France we serve both Startups and Fortune 2000 firms. We use a next generation Portal to combine the use cases of Digital Marketing, Fundraising and Application Development in tangible processes.







Leave a reply